In 2024, experts foretell that cybercrime will amount to $452 billion in companies in the U.S. a number that is set to rise instantaneously in the next few years. This makes it crucial for businesses to carry out strong cybersecurity measures in their operations.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the evolving area of cybersecurity thus stands as a formidable leverage to aid in reforming how we fight against digital threats. AI is an integral cybersecurity tool with instances ranging from network security to user validation through behavioural biometrics. AI can help combat cyber threats by aiding to detect, dissect, and respond to malicious attacks faster.
In this article, we are going to discuss the meaning of AI in cybersecurity, the pros and cons of AI in cybersecurity, and lastly, what the future of AI in cybersecurity is.
Meaning of AI in Cybersecurity
AI-powered cybersecurity is the act of using machine learning algorithms and advanced analytics to strengthen defence mechanisms and preventive techniques against cyber threats.

AI algorithms can inspect the entire network for drawbacks to deter common types of cyber attacks. It also analyses an enormous portion of data to detect patterns that signify a cyber threat.
AI has its perks but it’s important to know that it isn’t infallible. Therefore, it is necessary to be aware of its pros and cons.
Pros of AI in cybersecurity
The following are some pros or advantages of using AI in cybersecurity:
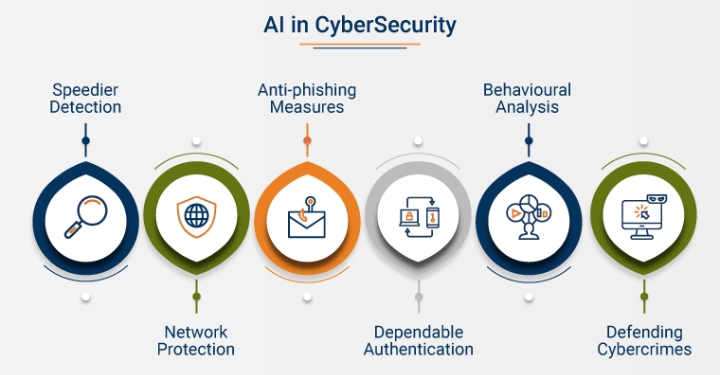
1. Threat Detection and Prevention:
These two, detection and prevention, are crucial elements of all cybersecurity systems. AI-powered strategies aid in quickly determining and neutralizing potential risks.
Furthermore, with AI algorithms, it becomes easier to monitor network traffic. It aids to recognise questionable patterns or deviations from normal behaviour.
AI can adapt to arising threats and new attack strategies that hackers frequently create. These strategies are meant to enable them to evade security tools and remain concealed while reducing false positives.
2. Faster Incident Response for Cybersecurity with AI:
This is something that AI tools can help businesses carry out to save time and money. Incident response is a process that involves cleaning up after a cyber attack. Usually, this time-consuming process requires a specialist skillset. There is also the need for a series of corresponding procedures to ensure that all systems are safe.
AI tools can help to make this process a lot easier. Also, it can help automate complex threat tasks like locking down data stores instantly.
3. Proactive Threat Hunting in AI-powered cybersecurity:
AI-powered security can fight new and emerging threats and also, improve your threat-hunting capabilities. With threat hunting, you can be preemptively defended from cyber threats.
The ability of AI to analyse large data makes it an excellent choice for threat hunters. With the use of the task execution and automation capacity of AI, threat hunters can process hunting queries based on contextual data.
4. Security Operations:
Regular tasks like log analysis and system monitoring can be simplified and enhanced with the use of AI. Also, the repetitive disposition of AI-based strategies guarantees ongoing modifications in threat detection and response, therefore, staying ahead of emerging risks.
In addition, these systems propose scalable solutions. This accommodates the exponential expansion of data and potential threats without compromising efficiency.
All these offer cybersecurity professionals the chance to focus on strategic initiatives.
5. Malware Analysis and Reverse Engineering:
Malware is frequently used by hackers to capitalise on susceptibilities. They also use it to acquire and retain access to compromised machines and extort victims for large amounts of money.
As a result, cybersecurity analysts to guard against this have to analyse and perform reverse engineering on it to discover new methods to protect against such occurrences.
AI comes in to analyse enormous volumes of malware samples, identify patterns, and the like.
Cons of AI in cybersecurity
Below is a list of some drawbacks of AI in cybersecurity:
1. Data Privacy and User Consent:
AI-powered cybersecurity is trained on extensive datasets of customers which contain network traffic, user activity, and even some sensitive information. This raises concerns about the privacy of users.
2. Malicious use:
Cybercriminals have found ways to make use of the vulnerabilities present in AI systems to evade detection or launch sophisticated attacks.
Furthermore, through the techniques devised by hackers and cybercriminals, AI systems carry out cyber attacks, scam unsuspecting victims, and generate malware.
3. Bias:
If trained on biased or incomplete data, AI algorithms are vulnerable to biases, and so, this could lead to inaccurate judgments by unfairly targeting specific users and overlooking probable threats.
4. Accountability:
Who is to take responsibility if AI systems make wrong judgments? Many AI systems are intricate and unclear. This makes it difficult to understand, and so, no one knows the true reasoning behind their decisions.
5. Security:
Flaws in AI models pose risks and could lead to exploitation by cyber attackers. Hackers could manipulate the data used to train the AI or exploit its weaknesses, and covertly extract sensitive personal information from the data.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
With AI, cyber threats can be detected faster, attacks can be predicted before they happen, and automatic responses to cyber threats. By leveraging its capabilities, businesses can bolster their walls against cyber attacks.
The trends emerging project that there will be advancements in AI algorithms and better integration with other cybersecurity measures.
Conclusion
The integration of AI in cybersecurity offers both promise and challenges. While AI can analyse enormous data, detect threats, respond to cyber threats, and the like, it has its limitations. It is, therefore, imperative for a balance to be struck between AI’s capabilities and human expertise in defending against future cyber threats.